From shoes and clothing, to bags and belts: Over 2 million metric tons of PU based artificial leather was produced in 2016, and almost all was manufactured using DMF coagulation, the process in which a paste with very high levels of the toxic solvent DMF (dimethyl formamide) is applied to a textile fabric and then dried. This meant that in 2016 the production of artificial leather used several hundred thousand tons of toxic DMF. In recent years however, considerable efforts are underway to establish other, more eco-friendly processes for the production of PU-based artificial leather.
Currently two processes are under consideration that provide very promising alternatives to DMF coagulation in the production of artificial leather. The first concept uses foamed, water-based polyurethane dispersions as a coating material during the leather production (water-borne process). The second is completely solvent free, and uses reactive polyol – isocyanate mixture as coating material (2K process). Both processes show significant improvements in reducing environmental impact, and are currently gaining increasing market share over the more established DMF coagulation process.
For waterborne processes, our KAIYUE TECH R&D can provide tailor made additive solutions. For PUD-based artificial leather, we developed additives that help support the foaming of water-borne PU dispersions. These include foam stabilizers, for example our KAIYUE product series, but also include a range of viscosity enhancers, and dispersing agents. For the production of 2K artificial leather our product portfolio includes tailored silicone surfactants (e.g. for cell regulation or improved leveling properties) as well as curing catalysts that help too control the reactivity of the PU coating.
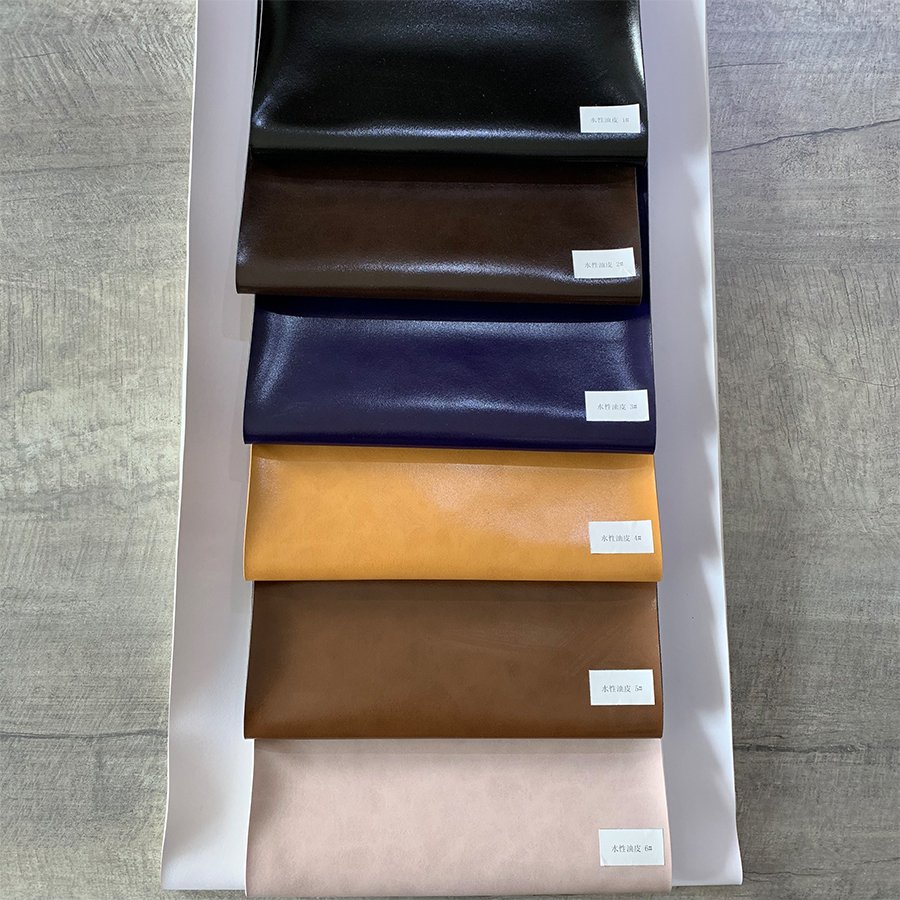 Waterborne PU oil leather
Waterborne PU oil leather
 KY-1100:KY-E1100烷芳基硅油
KY-1100:KY-E1100烷芳基硅油
 Wax feeling bright surface treatment agent KY209G
Wax feeling bright surface treatment agent KY209G
 KX-396C Leather surface treatment agent waterbonre PU Nubuck leather
KX-396C Leather surface treatment agent waterbonre PU Nubuck leather
 KYS-392 Waterborne low temperature Yangbuck Resin
KYS-392 Waterborne low temperature Yangbuck Resin
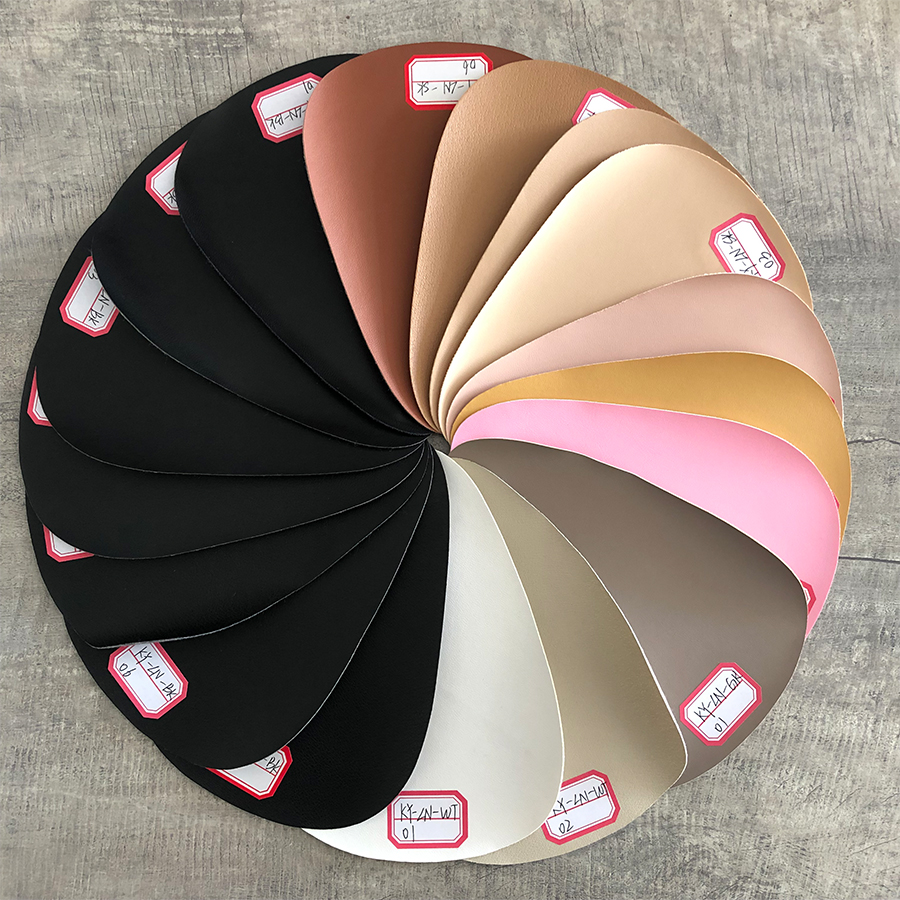 For shoes Lining
For shoes Lining
 DT-3305 PU leather garment leather hot and bright treatment
DT-3305 PU leather garment leather hot and bright treatment
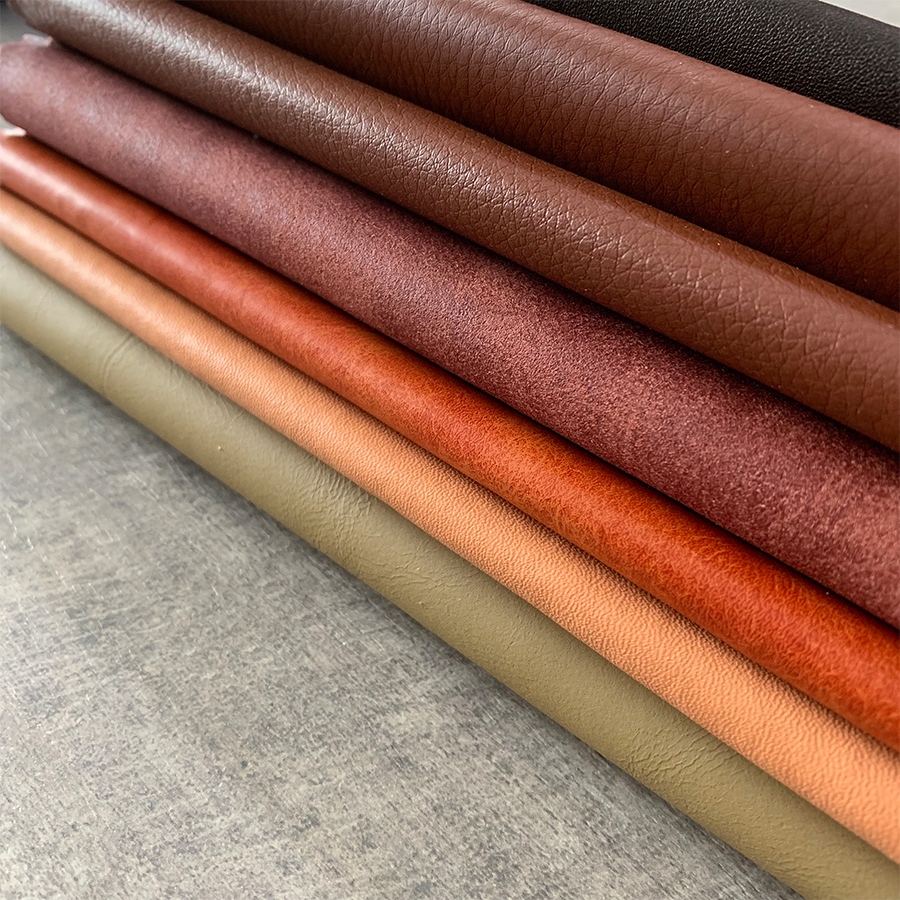 Microfibre
Microfibre